
Tremendous health problems and illnesses are now being detected and treated in novel ways thanks to healthcare data analytics. Now, it’s more important than ever to get to know a patient inside and out so that any potential health problems may be spotted and dealt with before they become serious.
With the help of technical revolutions like healthcare software development, predicting, identifying trends and patterns, gaining actionable insights, and limiting the spread of illnesses have been possible. This involves executing a variety of analytical operations on both historical and real-time data.
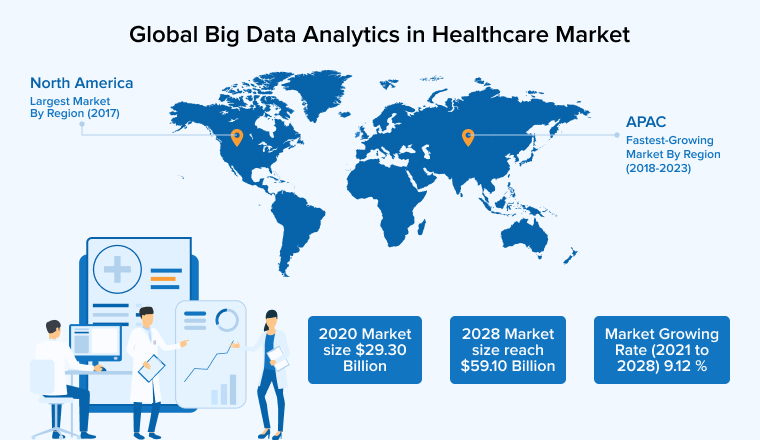
In this post, we’ll go over what is meant by “Healthcare Data Analytics” or Healthcare Analytics, some of its applications, and the role of visual analytics in Healthcare Analytics.
1. What is Healthcare Data Analytics?
Health data analytics is the practice of examining data with a variety of tools with the purpose of spotting patterns and trends that can then be used to inform and direct decision-making. Controlling and monitoring the spread of illnesses is the primary application area for Healthcare Data Analytics.
Analytical rigor in data collection and processing is the backbone of healthcare data analytics. The term “data analysis” is commonly used to describe the method of processing data sets in order to gain useful insights that can be used to guide better business decisions.
Healthcare professionals in the Healthcare industry may use data visualization in the same way that it is employed in any other industry. Data Analytics is practiced to conduct in-depth data analyses and show complex data in a way that is easy to understand and interpret. Patient care attempts, positive/negative feedback, or any other real-time information that might aid in decision-making could all form the basis of an assessment of the data.
When it comes to improving patient outcomes and operational efficiencies, the healthcare sector generates a massive quantity of data but has trouble turning it into actionable insights. One goal of data analytics in healthcare is to remove roadblocks to data’s widespread use for clinicians. Following are a few more:
- Facilitating the exchange of healthcare information between internal and external stakeholders and the visualization of such information for the general public.
- Allowing healthcare providers to adapt more swiftly to shifting healthcare markets and settings through the provision of accurate data-driven projections in real time.
- The automation of low-impact data management operations is improving healthcare companies’ ability to collaborate on data and generate new ideas.
2. Types of Healthcare Analytics
Unfortunately, the same data analysis won’t work for every inquiry. Many problems in healthcare may be answered with the help of big data analytics. Below are major types of data analytics in healthcare.
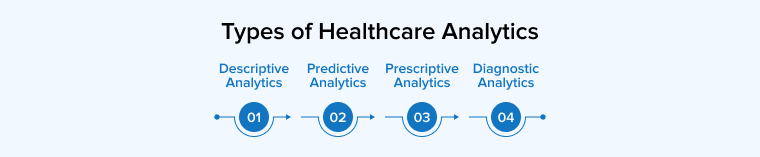
2.1 Descriptive Analytics
In order to make comparisons or find predicted trends, descriptive analytics examines data from the past. Questions regarding the past are best tackled using this method of investigation. Descriptive analytics allows you to better understand the past.
2.2 Predictive Analytics
Data from the present and the past are analyzed in order to foretell what will happen in the future; this is what predictive analytics does. Questions regarding the future are particularly well suited to the predictive models generated by this sort of analytics.
2.3 Prescriptive Analytics
The results of prescriptive analytics will be predicted as well. This kind of analytics relies heavily on machine learning. With this data, you can make an educated decision on what to do next. With the help of prescriptive analytics, you can figure out what steps need to be followed to achieve the best possible results.
2.4 Diagnostic Analytics
Similar to descriptive analytics, diagnostic analytics examines the past to provide an explanation. Diagnostic analytics, on the other hand, shifts the emphasis from the “what” to the more pressing “why” of an event occurrence in a certain context. The goal of diagnostic analytics is to pin down what made something happen.
Diagnostic analytics are utilized in the medical field to determine the cause of a patient’s condition and arrive at a correct diagnosis.
3. Benefits of Healthcare Data Analytics
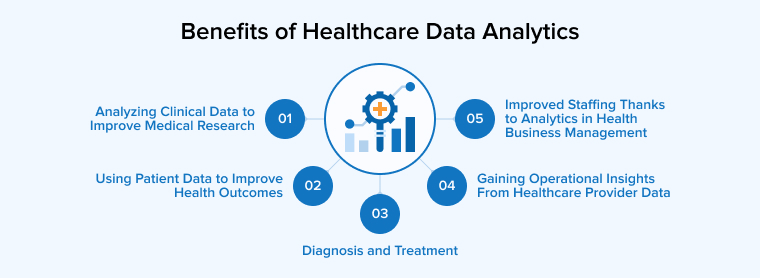
3.1 Analyzing Clinical Data to Improve Medical Research
By compiling and evaluating clinical data from a wide range of sources, data analytics methods are being used to advance research in many branches of medicine. Electronic health records (EHRs), electronic medical records (EMRs), personal health records (PHRs), and public health records are among the most helpful collections of healthcare data.
Electronic health records (EHRs) compile a patient’s medical history in a standardized digital format, including X-rays and other medical pictures, diagnoses, care planning, sensitivities, and test results. This facilitates communication but also adds privacy and regulatory compliance restrictions that restrict the data’s potential use.
Electronic health records (EHRs) are comparable to electronic medical records (EMRs), however EMRs only incorporate data from the patient’s paper charts maintained in medical facilities like doctors’ clinics and hospitals. Their primary significance is in documenting a patient’s healthcare history over several healthcare professionals’ appointments and screenings.
The patient, rather than a healthcare practitioner, is responsible for keeping track of the patient’s medical history in the form of a personal health record. It is important to note that these records are meant to supplement the patient’s personal health management, not to serve as a legal substitute for the official medical records that healthcare practitioners keep.
Researchers can benefit greatly from the information included in public health records. Examples include the Cancer Research Data Commons (CRDC) hosted by the National Cancer Institute, which is a cloud-based data science system that connects data analytics tools with information sources for genomic, biochemical, comparative oncology, radiology, and other types of data.
There are three main ways in which medical researchers might profit from data analytics:
- Researchers can use the findings to pinpoint potential avenues for streamlining hospital operations and enhancing the quality of patient care.
- The findings improve healthcare delivery by allowing more precise diagnosis and individualization of therapy.
- By tying together risk variables and health outcomes, cohort studies give doctors fresh perspective on chronic illness origins.
3.2 Using Patient Data to Improve Health Outcomes
Quality improvement in healthcare aims to reduce risks to patients while improving services. Healthcare providers gather and evaluate patient data, progressively in real time, to better comprehend today’s complicated health ecosystems; to create and employ a systematic strategy for improving patient results; and to build, test, and implement improvements to health systems.
Readmission rates, mistake rates, and the inability to detect at-risk individuals can all be reduced by examining patient data.
In this kind of analysis, data including a patient’s glucose level, temperature, medical tests, and treatment preferences are utilized. Primary determinants of treatment quality for patients include:
- A patient’s desired and most important health outcomes
- When and how a healthcare organization’s methods affect the results that patients want to see
- What role does the healthcare system, including its resources, equipment, laws, and other factors, have in determining the standard of treatment patients receive?
Getting immediate access to patient data that might help them enhance the quality of services they deliver is a major concern for healthcare providers. Concentrating on a few important performance indicators and collecting only as much data as is necessary to track those measures might help alleviate the stress caused by having too much patient information. The process involves qualitative evaluations of patient data and the provision of metrics that are easily available to physicians and can be monitored over time to identify and record progress.
In contrast to procedural measures of progress like unnecessary readmissions, hospital-acquired diseases, and fatalities, patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) are concerned with the clinical outcomes that actually concern to patients and that are:
- Complete healing after a severe illness
- Thriving while dealing with a long-term health issue
- Upholding human respect towards the end of life
Questions concerning the patient’s state of mind, pain levels, energy levels, ability to do daily tasks, and the severity of any symptoms are all part of the information gathered to evaluate the quality of services provided. It takes time and effort to obtain this information from patients, which slows the implementation of PROMs in healthcare settings. Because of the wide range of socioeconomic and demographic variables that affect patient outcomes, healthcare practitioners have a hard time drawing connections between patient-reported results and individual therapies.
The Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) was developed by the National Institutes of Health to assess and track patients’ emotional, psychological, and social well-being. The PROMIS Computer Adaptive Tests (CATs) are available for demonstration to healthcare providers in a number of different domains. These domains include unhappiness, anxiousness, distress, tiredness, pain behaviour patterns, pain intervention, physical function, and fulfillment with civil activities and social responsibilities.
3.3 Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis and treatment cycles for individual patients have varied widely from recommended clinical protocols. By studying these outliers, it may be possible to enhance the quality of treatment offered, boost patient safety as well as happiness, and fine-tune the app’s performance.
The improved availability of trustworthy data from health information systems allows for a better understanding of transit patterns and anomalies.
Simply put, Data Analytics has proven instrumental in improving the quality of care provided to patients and medical staff alike, hence reshaping the Healthcare sector.
3.4 Gaining Operational Insights from Healthcare Provider Data
The quality of treatment patients get and the probability of excellent patient outcomes are strongly influenced by healthcare practitioners’ work procedures and organizational structures. The capacity to gather and evaluate relevant data from healthcare providers relating to these procedures and structures is essential for assessing the impact of process and organizational changes on results and operational efficiency in today’s complex healthcare settings.
A healthcare system-wide evaluation of present circumstances and an integration of the institution’s plans and objectives for change are essential first steps toward enhancing healthcare excellence and cost. Scheduling, charts, emergency planning, accounting, financial management, and regulation are some of the most probable operational sectors to gain from data analytics.
Some methods healthcare organizations and clinics have implemented to cut costs without compromising quality of care are the following:
Getting Rid of Extraneous Stuff – Variability in clinical practices, improper patient care, avoidable care-related injury and death, and a lack of adherence to established protocols contribute significantly to healthcare waste.
Economical Application of Technology – Analytics and other cutting-edge tools are difficult and time-consuming to implement. Applying data analytics in a cost-effective manner requires a framework that isolates and prioritizes the processes with the most potential for growth.
Developing More Space in Hospitals – Instead of spending money on pricey new healthcare facilities, providers may save money by using analytics to better control the need for healthcare organizations wards and other healthcare services.
Enhancements to The Project Management Framework – Project management is becoming increasingly important in the healthcare industry as businesses embrace the Triple Aim framework developed by the Institute for Healthcare Improvement to optimize patient experiences and administrative effectiveness.
Preserving Gains in Performance – Data-driven healthcare improvement initiatives frequently fall short in allocating sufficient funds to maintain their gains. An organization’s analytics initiatives have a better chance of succeeding in the long run if all relevant parties are involved from the start.
3.5 Improved Staffing Thanks to Analytics in Health Business Management
To solve staffing problems and find qualified candidates for open positions, healthcare organizations employ data analytics. However, there is a rising scarcity of skilled medical personnel, which complicates efforts to reduce healthcare costs, increase efficiency, and better serve patients. About 60% of healthcare organizations expenditures are consumed by labor expenditures, and this proportion is likely to grow as the healthcare industry continues to expand.
In healthcare settings, data analytics is being used to control costs by maximizing the efficiency with which services are provided to patients. One of Hawaii’s major healthcare providers, Hawaii Pacific Health (HPH), saved $2.2 million over 16 months by using a data-driven method to labor relations while preserving quality results.
In place of HPH’s previous manual paper-based management system, new computer-generated visual representations of labor usage were implemented, providing both real-time views of staffing and visual depictions of staff levels. It allowed the hospital to cut labor expenses without compromising the quality of care delivered or patient outcomes by providing management with a clearer picture of the performance of individual employees and teams, as well as the cost-effectiveness of hiring considerations.
As a result of implementing an automated method for managing labor, managers now spend only 15 minutes out of every four hours on scheduling. The hospital has hundreds of employees who all utilize the same automated system to coordinate their shifts and access other work-related materials.
4. 4 Key Tools Used in Healthcare Data Analytics
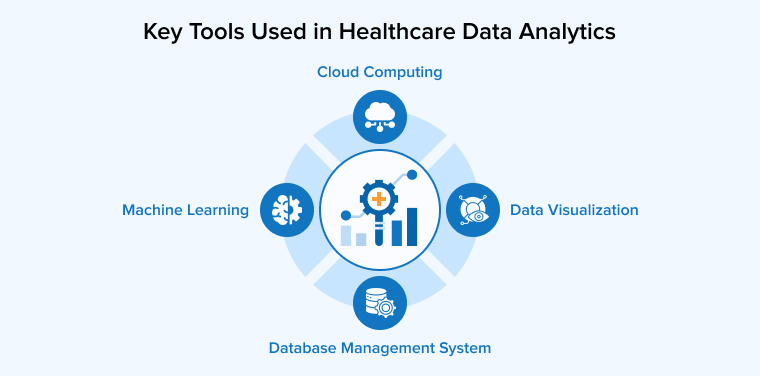
4.1 Cloud Computing
It’s no secret that healthcare IT deals with a lot of data. IT infrastructure is crucial for the effective storage and analysis of these data.
The capital outlay required for on-premise hardware and software is avoided when using cloud computing in Healthcare. The healthcare industry is always on the lookout for more scalable options, despite the fact that on-premise databases provide more control. Data warehouses are an instance of a cloud computing utility. A data warehouse is a central repository for all of an organization’s data, enabling rapid retrieval and analysis. Many similar services exist, including Google BigQuery, Snowflake, Redshift, and Amazon Athena.
4.2 Data Visualization
What researchers call “data visualization” is the process of displaying numerical and informational data in a graphical way. Data visualization tools allow users to explore data via the use of charts and tables. Health data analytics is another area where it is making strides. Data visualization solutions come in a wide range of prices, features, and subscription lengths. Those tools are:
4.3 Machine Learning
One of the most exciting fields of study is healthcare data analytics. Clinical data, omics data, and sensor readings are just a few examples of the many forms of data used in healthcare. Electronic health records (EHRs) are one type of clinical data that document patient information gathered during medical care. Genome, transcriptome, and proteome data are all examples of omics data, which is a sort of high-level data. The Healthcare industry makes extensive use of mobile and wireless sensors to gather and analyze data.
It’s challenging to work with this much raw data, but that’s exactly where Machine learning comes in handy. Machine learning incorporates a number of statistical methods and complex algorithms to improve the accuracy of health data prediction. Analyses in machine learning may be conducted with a wide variety of algorithms. These include supervised learning, unsupervised learning, the decision tree algorithm, and many more.
Integrating healthcare systems with qualified machine learning models can help medical personnel arrive at solutions based on patient data. It is much easier for doctors to decide what is best for their patients when they have access to healthcare IT systems that incorporate machine learning capabilities.
4.4 Database Management System
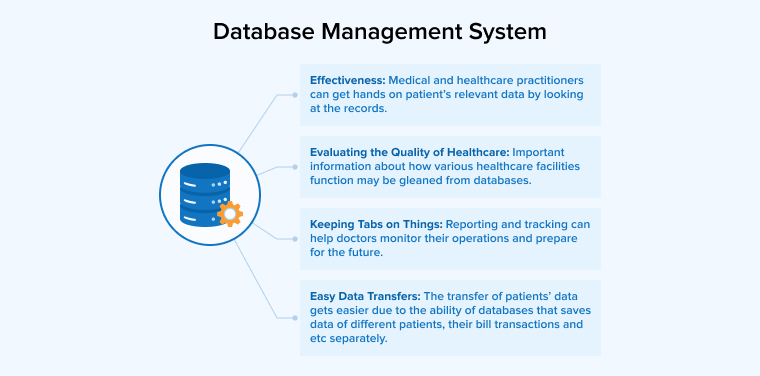
As the use of technologies in healthcare continues to expand at an accelerating rate, a robust database management system is essential for keeping track of all the new data being produced and making it easy to find when you need it. The information is stored and made suitable for data analysis by means of a Database Management System.
5. Some Challenges Involved in Implementing Healthcare Data Analytics?
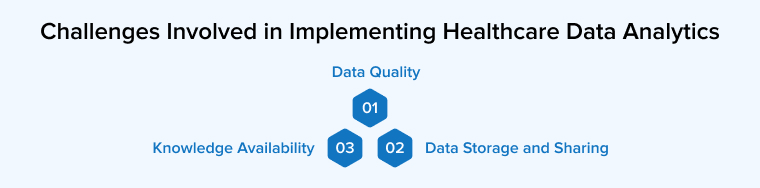
5.1 Data Quality
Check that the information you intend to gather is error-free, comprehensive, precise, and presented in a standard format that can be read and understood by a variety of platforms. You may avoid issues with data acquisition by making sure your EHRs are configured. Unstructured and in a variety of formats, healthcare data is a major challenge in the industry. Important details regarding patients, employees, and general performance are often found in this type of unstructured data.
5.2 Data Storage and Sharing
When thinking about the next step, keep data silos in mind. By combining your own, cleaned and standardized data with external data in a data lake or equivalent repository, you may identify the most promising areas for expansion and the steps you can take to take full advantage of them, resulting in value creation of previously unimagined proportions. Equally crucial, HIPAA-compliant clinical data must be safely distributed across various institutions like health facilities, medical clinics, ancillary providers, research labs, and more in order to formulate improved healthcare projects and optimal patient outcomes. As with any form of information sharing, concerns about individual privacy arise when people share their data.
5.3 Knowledge Availability
There is a large daily influx of data into healthcare institutions. Many hospitals, though, lack the means and expertise to make optimal use of their data since data scientists are in great demand and scarce. This gap may be closed by utilizing either sophisticated analytics services staffed by healthcare professionals or by utilizing analytics-enabled tools that provide insights and optimum next steps.
6. How Does Healthcare Analytics Improve Patient Care?
Data analytics is frequently used to assist healthcare companies discover hidden causes of resource waste. Effective patient approaches rely heavily on the use of healthcare data and health analytics, which may guide the way in which marketers interact with individual diseases or groups of patients. Health care providers will be able to make better decisions about how to use their money, time, and energy to improve the health of their communities and their patients.
6.1 Medical Expenses
Efficiency and other positive results may be rewarded through value-based payment schemes. The inside and outside experiences of patients are crucial to understand patient and overall program expenses.
6.2 Risk Assessment
The expense of treating chronic illnesses is a substantial burden on the healthcare system. By recognizing patients with high risk early and assisting them in taking as much control as possible over their own healthcare. Predictive analytics may significantly save spending.
6.3 Evaluating Practitioner Performances
The introduction of healthcare data analytics gives new ways of evaluating the performance and efficacy of clinicians at the time of delivery, coinciding with the massive shift away from volume-based to value-based care. Practitioners might benefit from continuous feedback in the form of assessments of their performance and health data pertaining to the wellbeing of their patients.
7. Conclusion
The use of data analytics in the healthcare industry has led to systemic and individual benefits. It’s another area where numbers are king.
This article discussed the significance of data analytics within the healthcare industry. You were also exposed to the different healthcare softwares and hardware that contribute to Health Data Analytics. Still have doubts? Please drop them in your valuable comment box.






This article offers a comprehensive guide to Healthcare Data Analytics, delving into its various types, benefits, challenges, and essential tools. Thank you for sharing this informative resource!
The author's detailed exploration of types of healthcare data analytics, covering Descriptive, Predictive, Prescriptive, and Diagnostic analytics, proved immensely helpful. Thank you for sharing this valuable insight!