Software development is a very simple process that starts with system planning and ends with deployment. However, this process becomes more complex when the developers are tasked with creating enterprise-level software solutions instead of small products. The reason behind this is that building complex systems requires a comprehensive software development methodology and quality assurance services. That is why we have concepts like Software Development Life Cycle and Software Testing Life Cycle.
Both these approaches are useful for creating and managing a high-quality software product. They do have their differences and similarities. Let us understand these concepts in detail.
1. What is SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle)?
SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) is a process that every software development company follows to design, build, and maintain working software. SDLC process consists of various phases including planning, requirement analysis & gathering, software designing, implementation of designs & new approaches, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
Each of these phases has dedicated processes and deliverables. If you adopt the software development life cycle then you have to start from conception or ideation for the software by considering the requirements. SDLC is a strategic approach to ensure you build software in a systematic and well-defined manner. This helps software developers meet the customer’s expectations and deliver high-quality results.
Here is what Twitter user says about the software development life cycle.
A Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a structured process for:
— Fatima zarah 🌸🌷 (@fatoomtyzarah) November 1, 2024
Planning, designing, developing, testing, and deploying software.
Managing and maintaining software applications from conception to retirement.
Ensuring quality, reliability, and efficiency in software…
1.1 SDLC Phases
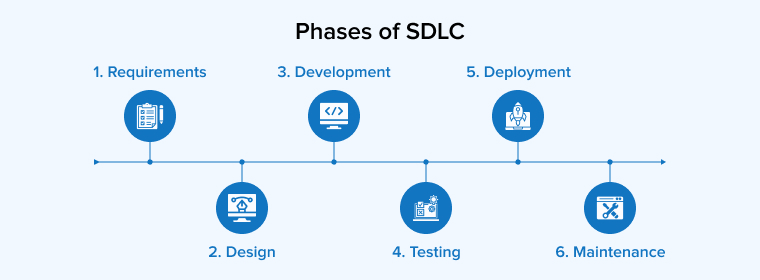
The essential stages of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) are outlined below:
- Requirements Gathering and Analysis
Development teams and project stakeholders gather to analyze the needs for the software project during this phase. Understanding the needs and demands of the end users—that is, customers—is the major goal here.
- Design
In this phase, the app architects consider the project requirements and draw out a suitable software design. It covers every little detail, every single functionality along with the architecture lying underneath. The designers also describe how your software will look on the client side and how its functionalities will work on the server side.
- Development
This stage involves writing programs that bring your software designs to reality. The developers write code to build different components and features of the software. The development process is often carried out in numerous sprints or iterations.
Here each sprint includes the creation of a single feature or component. In the end, all the components and features are integrated to form a fully functioning software.
- Testing
After completion of the development stage, the product needs to be validated as a single working system along with all its individual functionalities. Test the program thoroughly to identify and fix flaws in new features, ensuring that quality standards are met. Conduct retesting until the program meets the client’s requirements.
- Deployment
The software product is launched and made available to customers or end users once it has passed all testing phases and meets all quality criteria.
- Maintenance
The system is handed over to the team responsible for maintaining it for the duration of its existence at the workplace during the maintenance phase. For service desk workers to be able to send user support requests to the right team, the right paperwork and help files will need to be made.
1.2 Benefits of SDLC
Some notable advantages of using SDLC to create software include:
- Structured Approach
For developers, SDLC provides effective planning, organization of work, and a disciplined approach to software development. This systematic strategy not only reduces mistakes but also improves productivity, ensuring the timely delivery of high-quality software.
- Increases Visibility
Every phase of the SDLC has specific benchmarks and requires particular deliverables. Every activity is recorded, and each step is monitored. Stakeholders may therefore see development at each moment and see how resources are distributed in the name of the objectives.
- Manages Risks Effectively
SDLC is designed to reduce these kinds of risks in the software development process. Its methodical and structural approach begins with appropriate planning and implements many tests throughout every stage of software development. Such testing strategies first highlight possible project risks and greatly lower the project failure risk.
- Cost-Effective
Through the early identification of potential challenges using prototype tools like Figma and others, SDLC helps save development costs. Moreover, early identification of problems gives developers an opportunity act to resolve them, therefore lowering the general development expenses.
1.3 Key Features of SDLC
Some of the key features of SDLC are –
- It comes with detailed documentation of the functions, model structure, and test environment.
- SDLC offers an efficient risk management concept that can be utilized by software developers to reduce their risk exposure.
- It provides a step-by-step approach to software development and testing, which helps in completing the project before the deadline.
- With SDLC, the developers, designers, project managers, and business analysts get a clear understanding of their roles and responsibilities in the project.
- It is a cost-effective process.
1.4 Why SDLC?
Here are the reasons that show why one must choose SDLC in software development-
- SDLC aims to deliver high-quality software applications as per the client’s expectations.
- This process ensures that all the stakeholders are aware of the project and its planning.
- Each phase of SDLC is followed by a formal review, which helps in effective management control.
- It helps you to create considerable system documentation.
- In every stage, including the testing phase, there are entry criteria, exit criteria, and specific deliverables.
- It offers management plan overhead and lowers project risk.
- Enables an efficient and faster software development process.
1.5 Software Development Life Cycle Models
Even if the customer has a vague idea of what they want, there are a variety of software development life cycle (SDLC) models that may assist bring the project to perfection.
| SDLC Models | Key Features | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Agile Model |
|
|
| Waterfall Model |
|
|
| V-Shaped Model |
|
|
| Iterative Model |
|
|
| Spiral Model |
|
|
| Big Bang Model |
|
|
2. What is STLC (Software Testing Life Cycle)?
STLC (Software Testing Life Cycle) is a process consisting of various activities to ensure that the software’s quality is up to the mark. This is a part of the software testing process. The software testing life cycle process is performed by the testing team which ensures the quality of the applications.
STLC ensures that each new release rolls out smoothly and successfully. It is known as an important and integral part of the SDLC. But it only applies at the time of test phases. The stages of STLC may be repeated multiple times while the project is being developed before it goes into the software deployment phase. Besides this, an analysis is conducted of all the different tests in the STLC process and it is documented. This is known as a test closure.
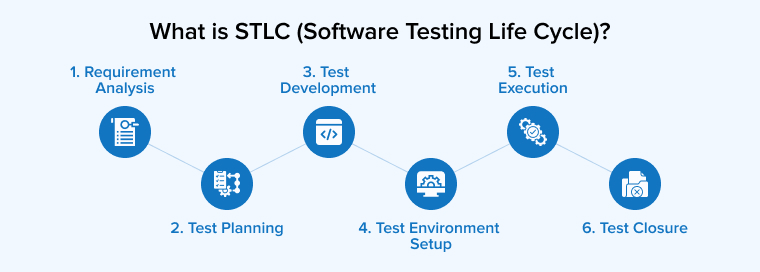
2.1 STLC Phases
| STLC Phases | Procedure |
|---|---|
| Requirement Analysis |
|
| Test Planning |
|
| Test Development |
|
| Test Environment Setup |
|
| Test Execution |
|
| Test Closure |
|
2.2 Key Features of STLC
Some of the key features of STLC are –
- It determines the system testing type and method.
- STLC analyzes the system requirements that the software development team gathered from clients and stakeholders.
- The STLC process helps in developing a traceability matrix.
- Helps in prioritizing the software feature that needs to be tested the most.
- Describe the test environment setup.
- Assesses automation feasibility.
2.3 Benefits of STLC
There are many reasons to adopt the Software Testing Life Cycle for your project. Here are a few:
- Early Detection of Defects
During the early phases of software development, the STLC initiative was implemented. This means that errors can be discovered and resolved before they evolve into more severe issues later on. This method addresses problems when they are less costly to fix, therefore saving both time and money.
- Enhancing User Experience
High-quality software delivers a good user experience. By identifying and resolving usability issues, software testing ensures that users can quickly and successfully engage with the system.
- Reduced Development Costs
Early in development, catching errors is considerably less expensive than making repairs later on. By addressing significant issues that delay releases, STLC speeds up time-to-market and reduces post-deployment rework.
- Enhanced Software Quality
Early in the development process, STLC actively analyzes and fixes issues to ensure that the tested software system performs as expected and follows the given standards.
2.4 Why STLC?
Here are the reasons that show why one must choose STLC in software development:
- STLC helps various testing teams to carry out quality improvement activities in different ways.
- It is easy to understand and implement, regardless of the development phase or testing processes.
- In STLC, the execution phase develops a high-quality software release.
- Here tests are conducted on each module of the software before the closure of successful software development.
- It helps in improving the efficiency, and consistency of the software testing process.
- Software testing life cycle helps in improving the quality of the software development.
- It helps in removing the flaws of the software at the early stage.
- STLC assures that clients and end-users of the product receive the best results.
- It helps in optimizing the quality control in the entire SDLC process.
3. Difference Between SDLC and STLC
Let’s have a look at the difference between SDLC and STLC –
| Parameters | SDLC | STLC |
| Definition | Software Development Life Cycle is a process that mainly focuses on developing software that can meet the client’s expectations and work efficiently in the technological infrastructure. Besides, it is a cost-effective process. | Software Testing Life Cycle specifies what type of test activities must be carried out and when should the testing team accomplish those test activities. |
| Relationship | SDLC is taken as the predecessor. | STLC is taken as the successor. |
| Focus | The focus of SDLC is on complete software development including the testing process. | The focus of STLC is only on the testing process. |
| Phases | The SDLC phases are Requirement Gathering, System Analysis, Software Designing, Coding, Software Test Execution, and Deployment & maintenance. | The STLC phases are Requirement Analysis, Test Planning, Designing of Test, Environment Setup, Software Test Execution, and Test Cycle Closure. |
| Requirement Analysis Phase | In SDLC, the business analyst collects all the requirements and creates a software development plan. | In STLC, the QA team analyses requirements and creates a perfect system test plan. |
| Design Phase | The SDLC team creates the high and low-level designs as per the project’s requirements. | The test lead or test architect creates the test strategy. |
| Coding Phase | In the coding phase, the software developers create actual code. | The STLC testing team prepares for the test environment setup and executes test cases. |
| Testing Phase | Here the actual testing process starts which includes testing types like Unit testing, Integration testing, Regression testing, performance testing, etc. | Actual testing in this phase starts with defect reporting & retesting is done here. |
| Deployment or Maintenance Phase | In this last SDLC stage, the development team offers support and release updates. | The QA team executes regression suites to check the deployment of maintenance code. |
| Environment setup | After the code has been produced, the team sets up a test environment to ensure it works as intended. | Developers review prerequisites and perform Smoke tests to verify the test environment is ready and stable. |
| Maintenance | Support, improvement, and update services after deployment are covered if required. | When checking the newly released maintenance code, the QA team conducts regression testing. The team keeps test cases and automated scripts updated to guarantee accuracy. |
| Team size | We required more programmers to help with the software development life cycle (SDLC). | The number of testers required to complete the STLC process is smaller compared to SDLC. |
| Outcome | The outcome of SDLC is that users can get a high-quality software system. | The outcome of STLC is that the users can get bug-free software. |
4. Conclusion
As seen in this blog, both SDLC and STLC are the most important aspects of a software development project for creating a perfectly reliable and secure system. SDLC is a methodology that offers a structured and phased approach to product development while STLC validates the projects for their reliability, performance, and functionality.
Though there are many differences, SDLC and STLC have some similarities as well such as gathering requirements, working in iterations, and a common objective of providing high-quality deliverables. More importantly, it’s a well-known fact that testing the life cycle is an integral aspect of the development life cycle.






Thank you for sharing this insightful article on the Difference between SDLC and STLC. Both are integral components of the software development process and this article provided deep insights into these two cycles, their stages, and how they work.
Your comparison of the SDLC and STLC is really insightful, in my opinion. I concur that a software development project's optimal method will rely on the particular requirements of the team and the organization. I would also add that it is crucial to be adaptive and flexible because a project's requirements may alter over time.
For any software development team, it is essential to have a deep understanding of SDLC and STLC. However, they have different goals and objectives, and the best approach will vary depending on the specific project. This article is well-written and provides complete insights into these two methodologies. As a software developer, I appreciate this comparison.