Related Blogs
There are many points that need to be considered when moving from a standard enterprise application deployment model to a cloud computing model. There are 2 major options to choose from: Private cloud vs Public Cloud. Often, the users are confused about whether to choose a public cloud or create a private cloud for their business due to privacy, security, and maintenance issues. In this article, we will try to focus on the benefits of each type and to derive conclusions.
1. Public Cloud
A public cloud is a standard cloud computing model wherein a service provider manages storage and computing resources on behalf of consumers over the Internet. The term “public cloud” arose to differentiate between the standard model and the private cloud, which runs on a proprietary network or data center of the user.
Public clouds are run by third parties, and applications from different users are shared on the provider’s cloud servers, storage systems, and networks. Public clouds are most often hosted away from customer premises, and they try to reduce customer risk and cost by substituting their enterprise infrastructure. Benefits of public clouds include ease of on-demand scalability as they are larger than a company’s private cloud. In public cloud deployments, It also shifts infrastructure risks from the enterprise to the cloud provider as all the resources are managed by the provider only.
Public cloud has raised some security concerns for businesses that have regulatory compliance requirements. It includes security against hackers and Security against resource contention. As in public cloud, resources are shared between various users over the internet; they are the major target of attack for hackers. In resource contention issue, as the public cloud contains shared resources which can expose all users in the cloud to security risks when any user becomes the target of a Denial of Service (DoS) attack.
Applications which are required for temporary purposes or for short duration are the best suitable for deployment in a public cloud because it avoids the need to purchase additional equipment to solve a temporary need. With public cloud, Customers can take advantage of various services such as computing power, storage space, on-premises infrastructure, etc. The largest public cloud providers include Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), IBM’s Blue Cloud, Google AppEngine and Windows Azure Services Platform.
2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Public Cloud
Let’s explore some pros and cons of the public cloud.
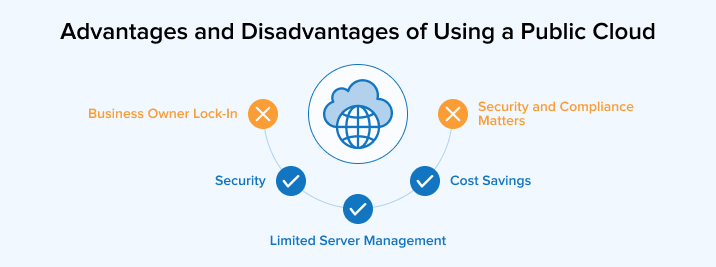
2.1 Advantages of Using a Public Cloud
Below are a few advantages of using public cloud services.
Cost Savings
Now companies are moving towards public cloud services to cut down IT operations expenses. That means most enterprises are outsourcing these charges to a third party who is skilled enough to manage them efficiently.
Public clouds are more affordable compared to private clouds because the cloud provider can grow their practice of hardware and their earnings by marketing their services to various customers at the same time.
Limited Server Management
If a company practices a public cloud, in-house teams are free from spending their time managing servers – which they have to do on-premises data centers or for in-house private cloud services.And in this cloud infrastructure, minimal supervision is required.
Security
Several businesses might not have the resources to execute effective security measures. However, utilizing public cloud services, they can outsource a few features of cyber security to a broader provider with more cloud computing resources.
2.2 Disadvantages of Using a Public Cloud
Here are several notable disadvantages of utilizing public cloud services.
Security and Compliance Matters
Multitenancy is one of the concerns for businesses that require strict regulatory compliance measures. Multitenancy also has the possibility of a minor danger of data leakage, which is a case of sensitive data and it is way more dangerous than some businesses anticipate.
The chance is a little; as most cloud providers serve remarkably high-security measures.
Lastly, it can be hard to use the same security procedures for an organization’s in-house resources as well as for a public cloud that is moderately out of a company’s handle.
Business Owner Lock-in
It is one of the main concerns with cloud services. A company that uses the cloud will preserve cash and become more resilient, but it can be a downside as well because it’s reliant on the services of the public cloud providers such as the virtual machines, storage, apps, and technologies they render – to manage their business operations.
3. Private Cloud
The Private cloud (also called internal cloud or corporate cloud) is typically hosted on customer premises. With proprietary computing architecture, it provides hosted services to authorized users behind a company firewall. Thus the company has control over resources, data, security and QoS.
The company owns the infrastructure and controls how applications are deployed on it. Private clouds can be deployed in an organization datacenter or also at a colocation facility. Private clouds can be built and managed by a company’s own IT department or by a cloud service provider. Under private cloud services, a company can install, configure, and operate the infrastructure as per its requirement and demand.
Benefits of going with a private cloud are increased control and monitoring of resources, flexibility of customization, ability to recover from failure, and the ability to scale up or down depending upon demand. Private cloud is less vulnerable to hackers’ attack by restricting access to its resources to authorized users and administrators only. On the contrary of public cloud, private cloud provides businesses with inherent protection from DoS attacks through secured infrastructure. Private clouds also provide a path for future upgradation to the public cloud.
Organizations are still reluctant to go with private clouds because users still have to buy, build, and manage the infrastructure and thus do not benefit from CAPEX reduction. Due to these constraints, they cannot reap the full benefits of cloud computing.
A permanent application, or one that has specific requirements on quality of service or location of data, is most suitable to deploy in a private or hybrid cloud. Enterprise IT organizations use their own private cloud(s) for mission critical and other secured systems deployment.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Private Cloud
Some of the pros and cons of using a private cloud are as below.
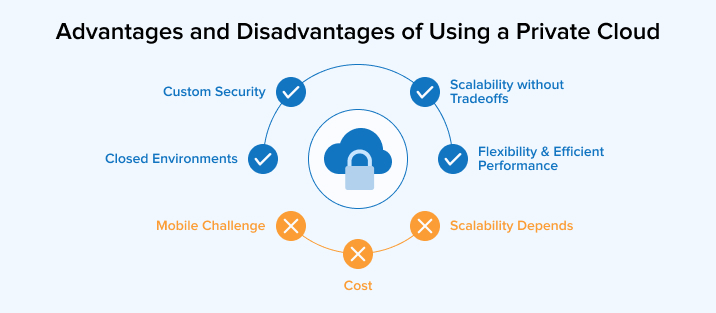
4.1 Advantages of Using a Private Cloud
Here is a list of benefits private cloud services have to provide.
Closed Environments:
Private clouds offer a dedicated and stable cloud environment that is not for everyone to use or other organizations.
Custom Security:
Agreement with valid management as organizations can manage protocols, cloud configurations, and patterns to customize protection based on different workload conditions. It also enables you to store sensitive data securely.
Scalability without Tradeoffs:
High scalability and performance to match variable requirements without negotiating on security and execution.
Flexibility & Efficient Performance:
The private cloud is responsible for leading SLA performance and efficiency.
The private cloud is flexible as you modify the support as per the ever-changing industry and IT demands of the business
4.2 Disadvantages of Using a Private Cloud
Here is a comprehensive list of drawbacks that private cloud services can offer to businesses.
Cost:
The private cloud is a costly solution with a moderately high TCO as opposed to public cloud options, particularly for short-term usage problems.
Mobile Challenge:
With a private cloud, Mobile users have confined access to the private cloud regarding the high-security standards in place.
Scalability Depends:
The infrastructure might not have high scalability to satisfy random requests if the cloud data center is bound to on-premise computing devices.
5. Private Cloud vs Public Cloud
| Sr. no | Differance | Private Cloud | Public Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Security | The infrastructure will get configured to give high levels of protection via private servers and a private network setting. | Providers render necessary protection standards with add-on safety options. |
| 2. | Performance | A dedicated server works inside the company’s intranet, which guarantees performance and reliable network execution. | Services are prepared instantly, allowing companies to preserve time. |
| 3. | Infrastructure | The complete infrastructure like hardware and networking is secured by the tenant. The infrastructure operates off-site as well as on-site. | The off-site public cloud infrastructure covers various tenants. |
| 4. | Affordability | The starting financing for hardware is expensive, challenging capital costs to install and manage. The investments involve buying all the hardware, installing it, and automatically operating expenses to support the infrastructure. | The first purchase is very inexpensive or nothing. There are no capital expenses. It’s either free or serves a freemium or pay while using the model. |
| 5. | Reliability | Infrastructure can be designed to cover contingencies. Resources can be redirected to other hardware like off-site or on-site in the case of a failure. | Public cloud companies such as Microsoft, Google and Amazon runs extensive networks that grow with state-of-the-art infrastructure protection. |
6. Conclusion
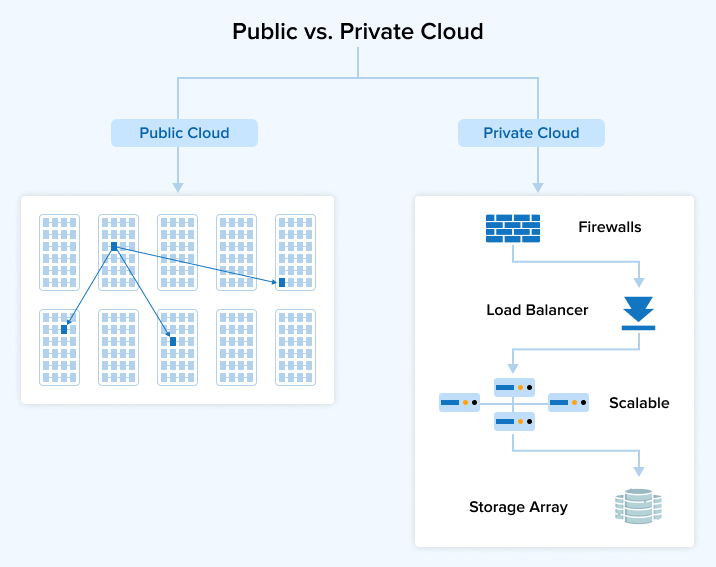
Below diagram shows difference between the private cloud vs public cloud in an easily understandable manner:
Please continue reading more on cloud computing at www.tatvasoft.com
FAQs:
What is the Difference between a Private Cloud and a Public Cloud?
A private cloud is something where one company has a hold of it and a single firm maintains and controls the entire infrastructure. On the other hand, the public cloud is known as an external cloud provider that offers the resources as a service.
What is an Example of a Private and Public Cloud?
Private cloud can be set up by companies in their own data centers or they can take the help of the hosting providers. Some of the best examples of private cloud providers are IBM, Oracle, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), and Dell, On the other hand, public cloud providers available in the market are Microsoft, Google, and AWS.
Is Azure a Private or Public Cloud?
Microsoft Azure is a public cloud where everything from software to hardware to other infrastructure options is owned by the cloud provider.
Is Oracle a Private Cloud?
Oracle Cloud is one of the most popular cloud computing services in the market offered by Oracle Corporation. This private cloud platform offers networks, servers, applications, storage, and a lot more to the clients. It also has its data centers which are managed by the Oracle Corporation. This platform offers on-demand services over the Internet.
Who Manages the Private Cloud?
A private cloud is managed by a third-party provider or the company that is using it. For instance, the IT infrastructure of an organization can be either purchased and maintained by a third party in its data center or by the company itself.

Vishal Shah
Vishal Shah has an extensive understanding of multiple application development frameworks and holds an upper hand with newer trends in order to strive and thrive in the dynamic market. He has nurtured his managerial growth in both technical and business aspects and gives his expertise through his blog posts.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Signup for our newsletter and join 2700+ global business executives and technology experts to receive handpicked industry insights and latest news
Build your Team
Want to Hire Skilled Developers?





Choosing from different deployment models in cloud computing is very important for software development. In this article, the author has provided a detailed comparison between two major types: Public vs. Private cloud. It has cleared a few of my doubts. Thank you for sharing!